FAQs on a Herniated Disc
What is a herniated disc?
A herniated disc, often referred to as a slipped or bulging disc, affects one in eight Americans between the ages of 30 and 50 years. Of this number, only a fraction is treated
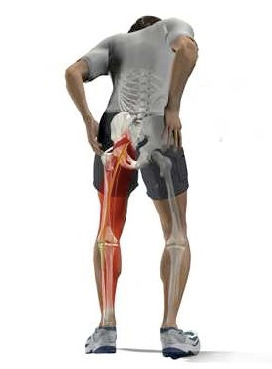
Sciatica results from a herniated disc in the low back pushing on a nerve root.
for the condition because a large number of cases go undiagnosed. Herniated discs can be extremely painful and grow progressively worse over time if left untreated.
A herniated disc is a problem that affects the rubbery cushion or disc that is situated in between the vertebrae along the spine. These individual bones stack up in order to create the spinal column, and the disc in between acts as a great shock absorber as a person moves, twists, and bends.
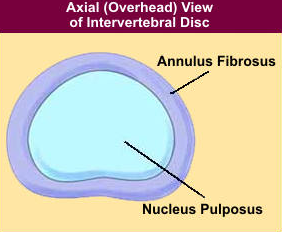
The disc itself has two parts, an inner part called the nucleus pulposus and an outer part called the anulus fibrosus. The analogy that is best is a jelly donut, where the inner part is softer than the outer shell. When a herniation occurs, some of the jelly that makes up the nucleus is pushed through a crack in the outer part of the disc. This problem can irritate the nerves located nearby and cause pain, irritation, tenderness, numbness and weakness in the extremities.
What are the symptoms of a herniated disc?
 You may not always know if you have a herniated disc because in some cases there is little to no pain. While herniated discs will show up on spinal imaging, some people do not know that they have a problem because no symptoms are exhibited. However, depending on the location of the herniated disc, some cases may be extremely painful.
You may not always know if you have a herniated disc because in some cases there is little to no pain. While herniated discs will show up on spinal imaging, some people do not know that they have a problem because no symptoms are exhibited. However, depending on the location of the herniated disc, some cases may be extremely painful.
Some of the most common symptoms associated with a herniated disc include:
- Radiating pain in the extremities – in the arms this is referred to as radiculopathy. In the legs this is called sciatica.
Pain that is isolated in the back and gradually radiates into the arms and legs, feet and hands, may be the result of a herniated disc. The pain may be stabbing in nature or dull, depending on the activity level at the time symptoms are noticed. It often feels like an 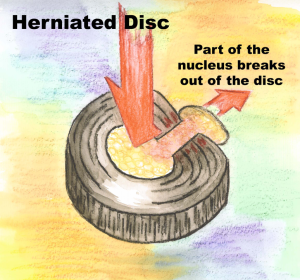 electrical sensation.
electrical sensation.
- Numbness or tingling
A common symptom of a herniated disc is numbness and tingling in the arms, legs, hands and feet. This prickly sensation can exhibit a pins and needles type pain and sensation.
- Muscle weakness
Extremity weakness of the muscles can be a symptom of a herniated disc and should be examined soon by NIPM pain management specialist who can determine the severity of the herniation.
When should you see a pain management doctor?
It is important to see your doctor if you experience neck or back pain that travels into the arm or down the leg. Radiating pain could indicate a herniated disc or a combination of other problems. If there is numbness, tingling sensations, or muscle weakness in the extremities or feet/hands, you should see your doctor right away.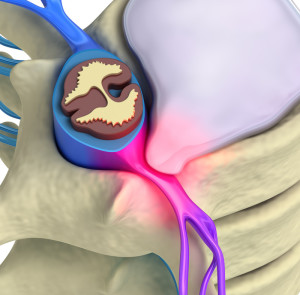
If you are experiencing bowel or bladder symptoms, that is an emergency and you should go to the emergency room. This is unusual, though, and typically the symptoms include pain and numbness and possibly some weakness.
What are the common causes of disc herniation?
The cause for this condition may be from gradual wearing of the disc, also referred to as disc degeneration. As a person ages, the discs in the spine lose some integrity. The discs lose water content that would otherwise keep them flexible and less susceptible to tearing. As the water loss occurs gradually over time, even a minor stretch, bend or twist may cause a minor tear in the disc.
Many people have trouble identifying the exact cause of the disc herniation because most times it is a gradual progression with age and wear-and-tear that leads to a rupture or tear. It is rare that a traumatic event, such as a motor vehicle accident or blow to the back can cause herniation.
Usually, it’s something minor like a sneeze or picking up a pen off a table or even just getting out of bed in the morning. The inner disc may just be waiting to herniate, and that minor event allowed the tear in the outer part of the disc to occur and allow the disc to squeeze out.
Are there risk factors that contribute to a herniated disc?
There are a variety of risk factors that make a person more prone to a herniated disc. These factors include age, weight and a person’s occupation or lifting activities. According

Truck driving may cause repetitive trauma to a disc and lead to a herniation.
to research published by the American Pain Society/American College of Physicians by Chou R, Huffman et al., 2007, herniated discs occur more often in middle aged and older men than any other population after strenuous activity is performed. The wear-and-tear of the muscles and disc degeneration through the aging process contributes to the problem.
Age-related disc degeneration is the most common risk factor for a herniated disc; however, obesity is also a major contributor. When a person carries excess weight on their body, especially in the abdomen, the lower back is affected. The added weight puts stress on the spine and discs in the back and neck, contributing to pain and possible disc herniation or rupture.
A person’s occupation and their daily routine can also contribute to a herniated disc. Physical demanding jobs that involve lifting heavy objects or throwing items overhead can cause wear-and-tear of the spine and muscles in the back. Repetitive pulling and pushing may increase a person’s likelihood and risk of a herniation.
What are the diagnostic tests use to locate a herniated disc?
A pain management doctor in Michigan will typically get a high suspicion of the diagnosis from the patient history. The physical exam often shows significant pain with a straight leg

Straight leg raise test will often cause pain exacerbation when a disc herniation is present.
raise test, which stresses the nerve roots in the lumbar spine. A complete motor and sensory exam will often elucidate where the problem is too.
Diagnostic tests may include:
- EMG
- CT scan of the spine
- Spine MRI
- X-rays of the spine
- Nerve conduction velocity exam
- Myelogram
All of the above diagnostic tests may be ordered to determine the location and severity of the disc herniation.
What treatment is available for a symptomatic herniated disc?
Initial treatment should consist of rest, ice and heat, over the counter NSAID’s and Tylenol, along with no more than 24-48 hours of bed rest. Studies have shown it is better to get back up and stay active as soon as possible.
Short term narcotics may be very helpful along with muscle relaxers and neurogenic medications such as Lyrica or Neurontin. A one time Medrol Dose Pak may be offered which provides a hefty dose of Prednisone for anti-inflammation. It should not be done in
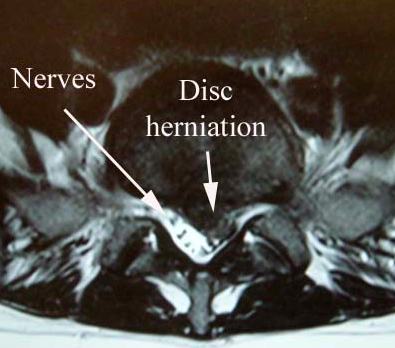
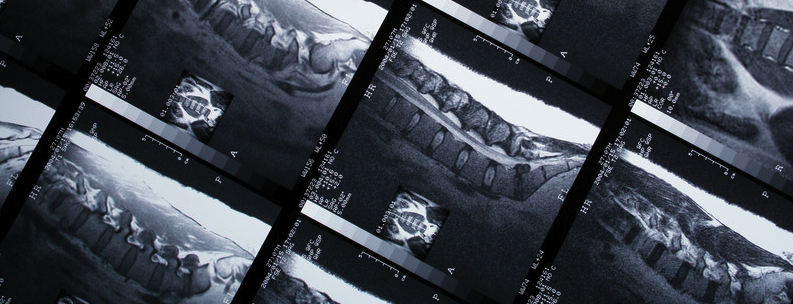
A large disc herniation seen on MRI.
conjunction with NSAID’s, as an ulcer may result.
Chiropractic and physical therapy may help relieve the pain along with spinal decompression therapy and a TENS unit. The decompression involves intermittent spinal traction with an FDA cleared table that is noninvasive and highly effective.
The gold standard for interventional pain management is epidural steroid injections. These are often performed as a series of injections (3 over a 6 week period) and may be repeated every few months.
The important thing to keep in mind is that none of the treatments for a herniated disc are designed to fix the problem. They all relieve pain, and often times the body will disintegrate the piece of disc that has herniated.
Surgery is reserved for those few individuals who fail 6 to 8 weeks of conservative treatment, and for those with progressive neurologic deficit or bowel and bladder issues.
What are the outcomes of treatment?
The vast majority of individuals with a disc herniation, over 95%, are able to avoid surgery with conservative treatment. A landmark study in JAMA showed that if surgery could be avoided, the outcomes were identical to those who underwent surgery after the one year point.
Epidural steroid injections work well 75-90% of the time, and spinal decompression therapy works well over 85% of the time. Often times a combination of treatments work best for optimal pain relief.


